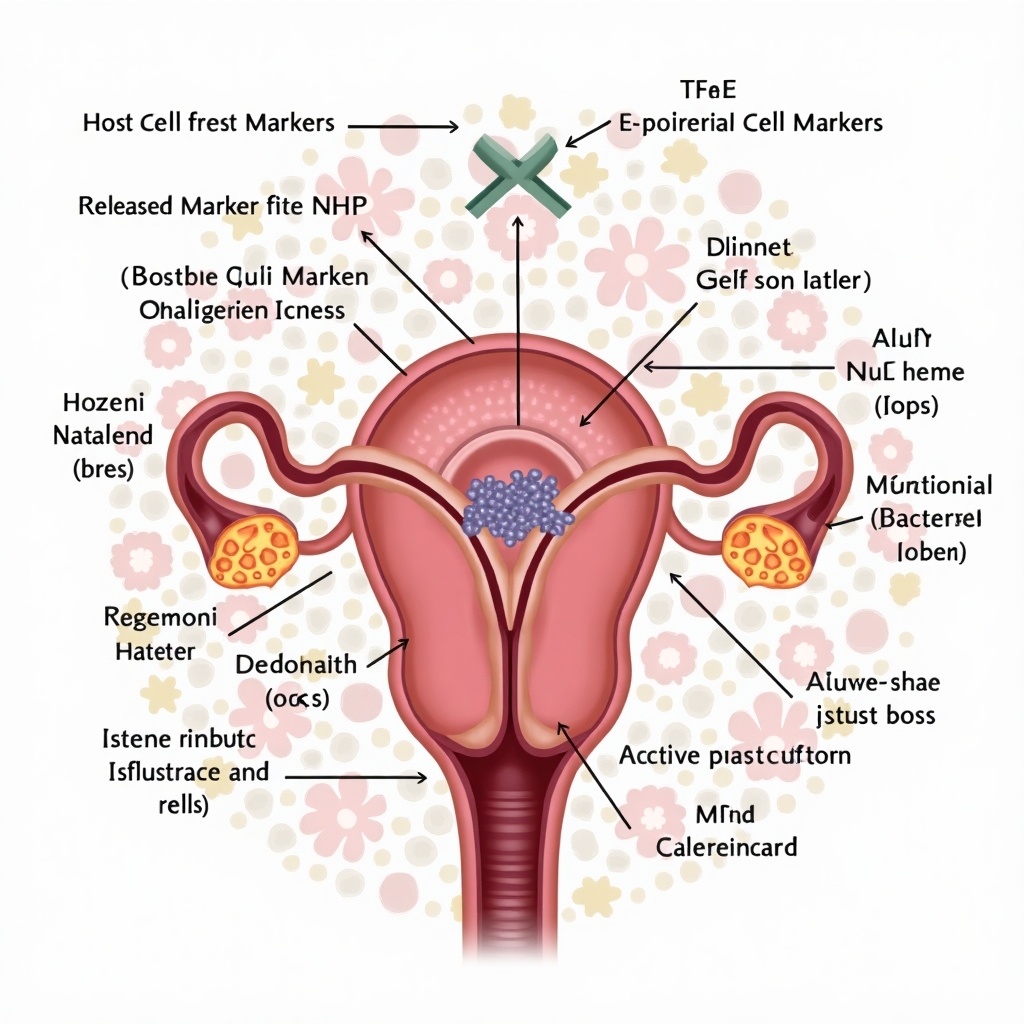
Structural Host Cell Markers: CD44, E-cadherin, uroplakin, Tamm-Horsfall Protein (THP) are critical in maintaining the structure and integrity of the urothelium. THP helps prevent bacterial adhesion, contributing to the urinary tract's innate defense mechanisms.
Markers Released from Host Cells: Prosaposin, NGF, HSP70, uMPO, PTX3, uB2MG, leptin, TREM-1, and exosomal markers (Akt, CD9) are released in response to cellular stress and immune activation. NGF plays a role in nerve sensitivity and may be associated with chronic UTI-related bladder pain.
Structural Bacterial Cell Markers: TLR2, TLR4, TLR5, and CD14/TLR complexes recognize bacterial components, such as LPS and flagellin, playing a key role in initiating immune responses against Gram-negative bacteria like E. coli.
Markers of Cellular Immune Response: Interleukins (IL-6, IL-1β, IL-17, IL-15, IL-10, IL-2, IL-9, IL-12, IL-13), chemokines (CCL2, CXCL8, CXCL1, CXCL9, CXCL10, CCL5), IFN-γ, TNF-α, CXCL12, FGF, SCGF β, PDGF, MIP-1α, and MIP-1β are all involved in the immune response to UTIs, recruiting immune cells to the site of infection, and promoting inflammation to combat bacterial pathogens.
Markers of Metabolites of Host Cells: K/T ratio and U-AGT provide information on host metabolic changes in response to infection, indicating alterations in immune regulation and inflammation.
Markers of Metabolites of Bacterial Cells: Acetate and trimethylamine are byproducts of bacterial metabolism, directly indicating bacterial activity and aiding in the rapid diagnosis of infection.
Acute Phase Reactants: uNGAL, KIM-1, CRP, PCT, copeptin, MPV, MxA are key markers of acute inflammation and stress. uNGAL and KIM-1 are particularly useful in assessing kidney injury associated with severe UTIs.
Other Markers: MMP9, YKL-40, BK channel activity, urine cloudiness, HD5, HNP1-3, RegIIIγ, HIP/PAP are additional markers that help understand tissue remodeling, bladder function, and the body's antimicrobial defense mechanisms. Antimicrobial peptides like HD5 and HNP1-3 directly contribute to controlling bacterial growth in the urinary tract, This image illustrates various markers relevant to host cells and bacterial interactions within the urinary tract. Key structural markers include CD44 and Tamm-Horsfall Protein (THP). Released markers show how the body reacts to infection, including Prosaposin and NGF. Bacterial cell markers like TLR2 help recognize pathogens. Immune response markers such as interleukins indicate inflammation levels. Metabolite markers provide insights into both host and bacteria activity, whereas acute phase reactants highlight inflammation and injury. This detailed illustration aids in understanding complex biological interactions